In this guide, we’ll explore cloud migration strategies, the key benefits, risks, and the essential steps for a successful migration. Whether you’re a small business or a large enterprise, understanding these strategies will help you make informed decisions.
🤔 What is Cloud Migration?
Cloud migration is the process of moving data, applications, and IT infrastructure from on-premise servers to the cloud. Businesses adopt cloud migration strategies to achieve scalability, cost savings, and improved security. However, to ensure a smooth transition, careful planning is necessary.
🌍 Why Migrate to the Cloud?
Migrating to the cloud has become essential for modern businesses. Here’s why:
✔️ Cost Savings – Reduce hardware, maintenance, and operational costs.
✔️ Scalability – Increase or decrease resources based on business needs.
✔️ Remote Accessibility – Access data and applications from anywhere.
✔️ Security & Backup – Cloud providers offer built-in security and data recovery options.
✔️ Improved Performance – Cloud computing ensures faster processing speeds and better user experiences.
However, without a proper migration strategy, businesses risk downtime, security issues, and operational disruptions. That’s why choosing the right cloud migration strategy is crucial.
☁️ Key Cloud Migration Strategies

1️⃣ Lift and Shift (Rehosting) 🚀
🔹 Best for: Businesses looking for quick migration with minimal changes.
🔹 How it works: Applications and data are moved to the cloud without modifications.
🔹 Pros:
✔️ Fast and cost-effective
✔️ Minimal disruptions to business operations
✔️ Works well for legacy applications
🔹 Cons:
⚠️ May not fully leverage cloud-native benefits
⚠️ Potential performance inefficiencies
2️⃣ Replatforming (Lift, Tinker, and Shift) 🔧
🔹 Best for: Businesses that want to optimize applications without major changes.
🔹 How it works: Applications are moved to the cloud with slight modifications to improve efficiency.
🔹 Pros:
✔️ Optimized performance in the cloud
✔️ Cost-effective while enhancing cloud benefits
🔹 Cons:
⚠️ Requires minor modifications
⚠️ May involve some downtime during migration
3️⃣ Refactoring (Rearchitecting) 🔄
🔹 Best for: Businesses looking for long-term cloud optimization.
🔹 How it works: Applications are completely redesigned to leverage cloud-native features.
🔹 Pros:
✔️ Maximizes performance, security, and scalability
✔️ Supports serverless computing and microservices
🔹 Cons:
⚠️ Time-consuming and expensive
⚠️ Requires significant development efforts
4️⃣ Repurchasing (Moving to SaaS) 💻
🔹 Best for: Businesses using legacy applications that need modernization.
🔹 How it works: Instead of migrating, businesses switch to a SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) solution.
🔹 Pros:
✔️ No need for infrastructure management
✔️ Regular updates and security patches
🔹 Cons:
⚠️ Data migration and vendor lock-in risks
⚠️ Customization limitations
5️⃣ Retaining (Hybrid Approach) 🔄
🔹 Best for: Businesses that cannot fully move to the cloud.
🔹 How it works: Certain applications remain on-premise, while others move to the cloud.
🔹 Pros:
✔️ Best of both worlds – cloud flexibility with on-premise control
✔️ Reduced risk and compliance issues
🔹 Cons:⚠️ Complex to manage hybrid environments
⚠️ Integration challenges
📝 How to Plan a Cloud Migration
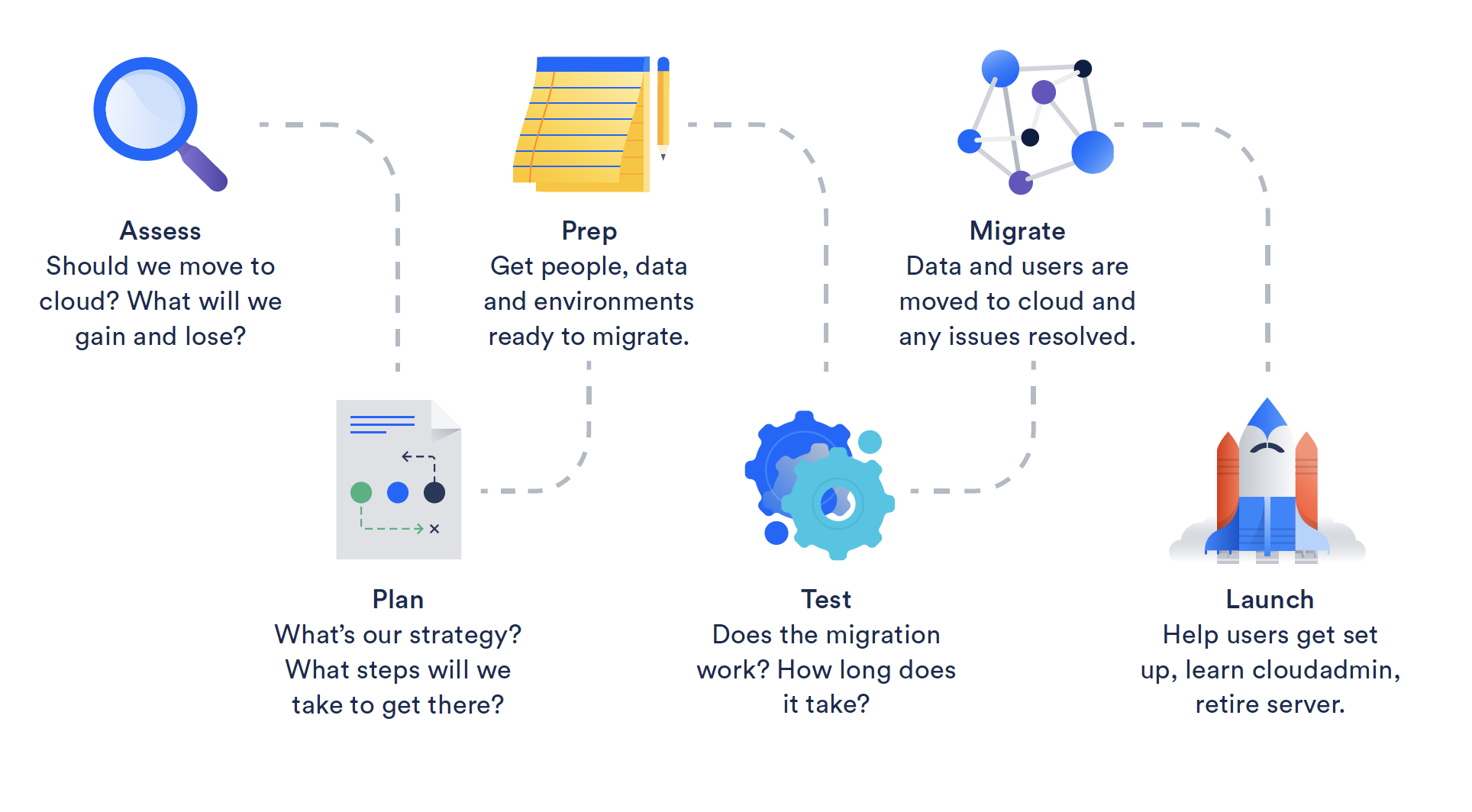
Planning a cloud migration requires a strategic approach to ensure a smooth transition while minimizing risks. The process begins with discovery and assessment, where businesses identify applications, services, and databases to migrate, map their infrastructure dependencies, and determine the best migration strategy—whether rehosting, replatforming, refactoring, or replacing workloads. Once the assessment is complete, organizations can use tools like the Cloud Foundation Toolkit to establish a solid cloud infrastructure, covering security, networking, resource management, and monitoring. A well-structured migration plan ensures scalability, security, and operational efficiency, making the transition to the cloud seamless and cost-effective. 🚀☁️
1️ Assess Current Infrastructure 🔍
- Identify which applications and data need migration.
- Evaluate on-premise vs. cloud compatibility.
2️ Define Business Goals 🎯
- What are your key objectives?
- Are you aiming for cost savings, scalability, or better security?
3️⃣ Preparation and Choosing the Right Cloud Service Provider ☁️
- AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud are popular choices.
- Consider SLA (Service Level Agreement) terms.
4️ Test Before Full Migration 🛠️
- Run a pilot migration for small workloads.
- Monitor performance and identify issues early.
5️ Develop a Migration Plan 🏗️
- Decide on a phased approach or big-bang migration.
- Schedule testing and backup procedures.
6️⃣ Monitor & Optimize After Migration 📊
- Continuously track cloud performance.
- Optimize for cost efficiency and security.
⚠️ Cloud Migration Challenges & Solutions
Even with the best cloud migration strategies, challenges may arise. Here’s how to tackle them:
🔹 Downtime Risks – Use a phased migration approach to minimize service interruptions.
🔹 Security Concerns – Implement strong encryption and access control policies.
🔹 Cost Overruns – Monitor cloud usage to avoid unexpected expenses.
🔹 Data Loss – Always back up critical data before migration.
🔹 Compliance Issues – Ensure your provider meets industry regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA).
🎯 Cloud Migration Strategies Final Thoughts
Cloud migration is a game-changer for businesses, but it requires careful planning and execution. Choosing the right cloud migration strategy ensures a seamless transition while maximizing performance, cost savings, and security.
🚀 Whether you opt for Lift-and-Shift, Replatforming, or a full Cloud-Native approach, understanding these strategies will help you avoid pitfalls and make the most of cloud computing.
Thinking about migrating to the cloud? Start with a well-structured plan and choose the right strategy for your business needs! 🌍☁️