🏁 Getting Started With WordPress
👀 Fresh Installed WordPress – Frontend Side
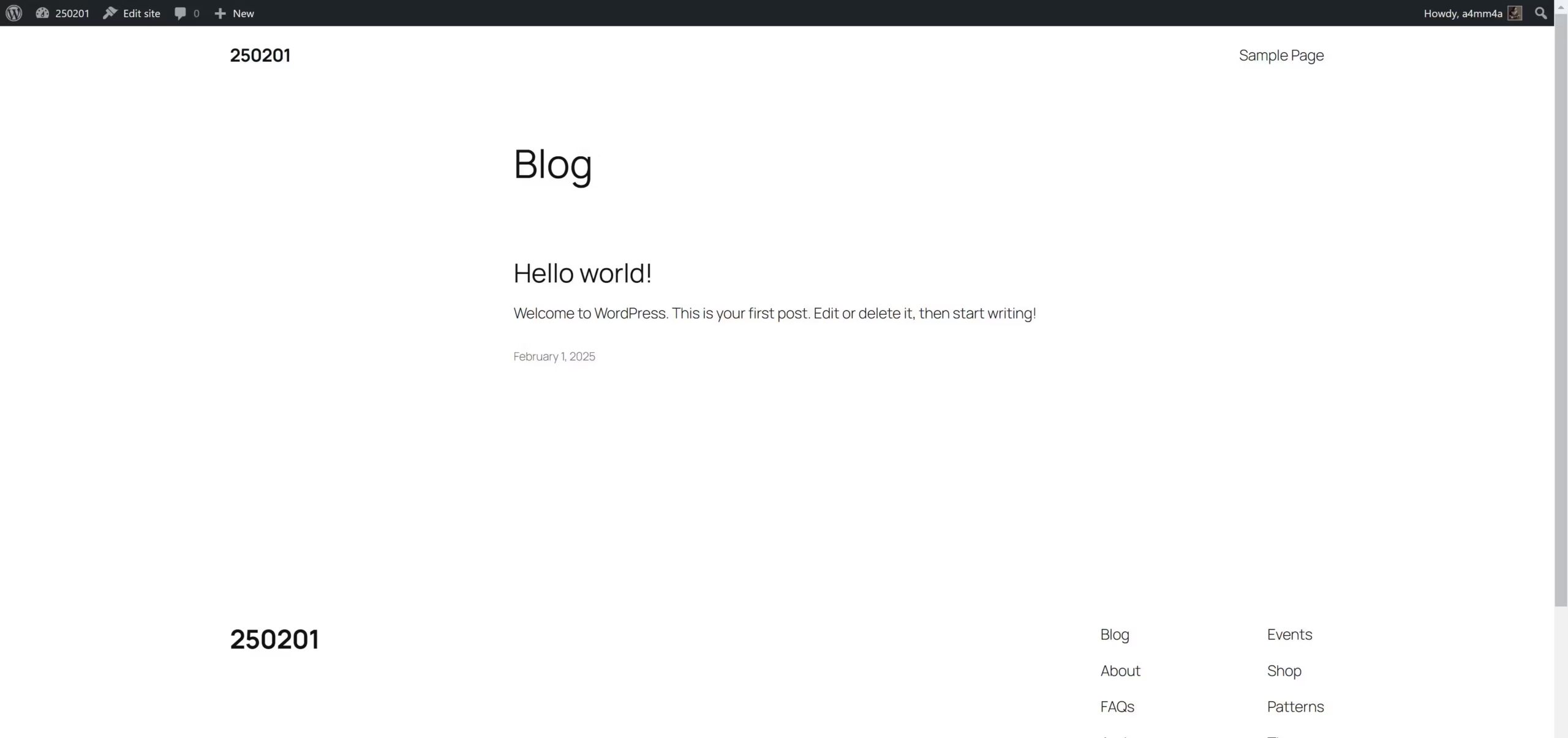
After installing WordPress, the frontend refers to what visitors see when they access your website. A freshly installed WordPress site has a default homepage with a simple layout, usually displaying:
- A sample post titled “Hello World!”
- A sidebar (depending on the theme) with widgets like Recent Posts, Categories, and a Search bar
- A footer area with default credits like “Proudly powered by WordPress”
🙌🏻 Accessing the Frontend
To view your site’s frontend, simply enter your domain name in a web browser (e.g., yourdomain.com). This is what your users and visitors will see when they visit your website.
🎨 Understanding Themes and Design
The appearance of the frontend is determined by your WordPress theme. WordPress comes with a default theme (like “Twenty Twenty-Four”), but you can change it later through the Appearance > Themes section in the backend.
🔙🔚 Fresh Installed WordPress – Backend Side
The backend is where you manage and customize your website. It is also known as the WordPress Admin Dashboard.
🙌🏻 Accessing the Backend
To log into your WordPress admin panel, go to:yourdomain.com/wp-admin
Enter your login credentials (set during installation), and you will be redirected to the WordPress Dashboard.
👀 Fresh Installed WordPress – Backend Overview
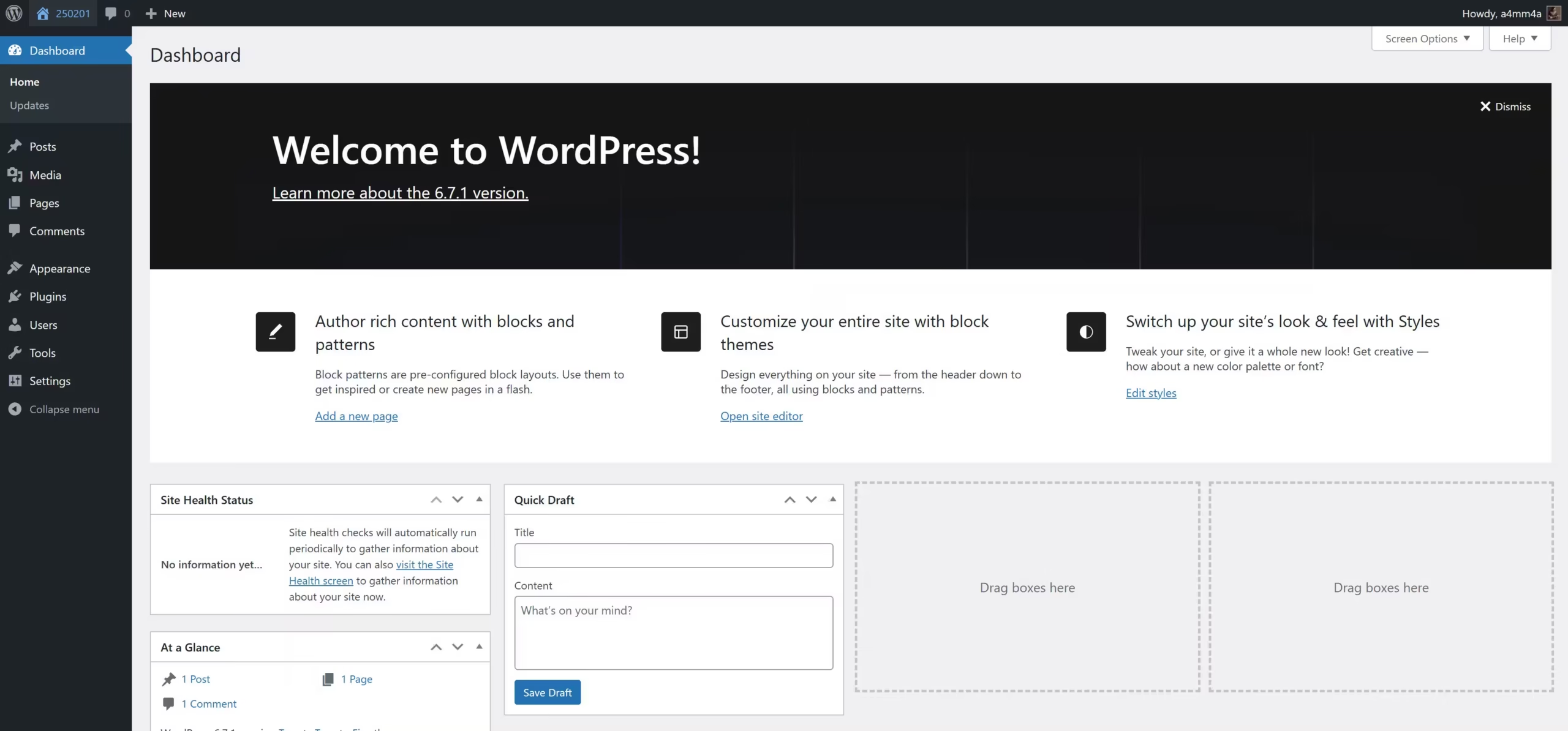
Once logged in, you’ll see the WordPress Dashboard, which serves as your site’s control panel. It contains:
- Admin Toolbar (Top Bar): Displays site links, updates, and user settings
- Main Dashboard Widgets: Quick access to site stats, recent activity, and drafts
- Left-Side Admin Menu: The main navigation menu for managing content and settings
At first, WordPress provides a simple interface, but as you install themes and plugins, new options will appear in the menu.
Fresh Installed WordPress Menus
Dashboard
- The Dashboard is your home screen after logging into WordPress.
- It provides quick links to important actions, recent activities, and WordPress news.
- The At a Glance widget shows how many posts, pages, and comments exist on your site.
Posts
- This is where you create and manage blog posts.
- Posts are dynamic content that appears in chronological order (useful for blogs and news websites).
- Includes categories, tags, and the Gutenberg block editor for formatting posts.
Media
- The Media Library stores all images, videos, and other uploaded files.
- You can add new media files and edit existing ones directly.
- Useful for managing content for blog posts, pages, and galleries.
Pages
- Pages are for static content (e.g., About Us, Contact).
- Unlike posts, pages do not use categories or tags.
- The block editor lets you format pages with images, text, and media elements.
Comments
- Manage comments left on your blog posts.
- Approve, reply, or delete comments directly from this menu.
- Helps in moderating discussions and engaging with visitors.
Appearence
- Controls the design and layout of your site.
- Includes:
- Themes – Change the look of your site.
- Customize – Modify theme settings like colors, fonts, and logos.
- Widgets – Add extra content to sidebars and footers.
- Menus – Create and arrange navigation links.
Plugins
- Plugins extend WordPress functionality (e.g., SEO, security, contact forms).
- Add, activate, or deactivate plugins from this menu.
- Essential plugins include Yoast SEO, Elementor, and WPForms.
Tools
- Import/export WordPress content.
- Site Health tool for checking performance and security.
Users
- Manage user accounts and roles (Administrator, Editor, Author, Contributor, Subscriber).
- Add new users with specific permissions.
Settings
- Control general site settings like site title, URL, reading preferences, and permalinks.
- Customize how posts and pages appear in search engines.
🚀 Next Steps:
👉 Explore each WordPress menu in detail
👉 Learn how to manage content, themes, and plugins
👉 Customize settings to optimize your website